
- products: brazed | double wall brazed | shell and tube | shell & coil | pool heaters | air to water
- applications: radiant floor heating | snow melting systems | district heating
 Heat
Exchangers for District Heating
Heat
Exchangers for District Heating
We supply shell and coil heat exchangers for district heating or energy systems that distribute heat from one or more heating sources to multiple buildings. As a centralized heating network, district heating systems promise a much more effcient use of existing energy sources and the recovery of wasted heat using heat exchangers. Our unique shell and coil design is the perfect fit for a district heating system that requires high performance reliablity, compact space-saving design and low maintenance costs.
Characterized by their circular layers of helically corrugated tubes encased in a shell, this heat exchanger is optimally suited for the water-water and steam-water environments found in district heating systems. District heating and cooling is swiftly gaining credibility as an economically sustainable source of energy for space heating, domestic hot water heating, air conditioning and other industrial purposes. Environmentally sound, energy efficient, reliable, easy to operate and maintain, district heating offers thermal comfort at a reduced price. Our heat exchangers are easy to install and will help you meet your energy needs even more efficiently at a much lower cost.
How
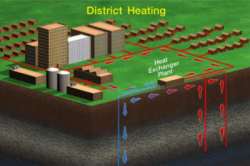
Shell and Coil Heat Exchangers Work in District Heating Systems
A
district heating system distributes heat or cooling from a single source
to multiple buildings including everything from private residences, hospitals
and schools to recreational buildings, municipal libraries, apartment
buildings and government office buildings. In a typical district heating
system, hot water is obtained from a heat generating plant, or in the
form of recovered heat from a nuclear power plant. (Other sources include
geothermal, cogeneration
plants, waste heat from industry, and purpose-built heating plants) The
heat from this hot water is transferred to the district heating network
using shell and coil heat exchangers maximizing the heat that is transferred.
On its arrival to the internal
heating systems of the designated buildings, heat from the hot
water is transferred to hot water taps, space and even radiant floor heating
systems. All of this is accomplished using heat exchangers specifically
designed for the available space and required heat load. The cooled water
then flows back to the original heating plant where it is reheated and
recirculated through the system.
For more information about district heating and cooling or district energy visit The International District Energy Association.
 The
Benefits of District Heating and Cooling:
The
Benefits of District Heating and Cooling:
The benefits of district heating and cooling are twofold. It centralizes
the source of heat into a single source, i.e., a nuclear power plant,
which, among other things, means lower capital investment costs in traditional
energy equipment such as furnaces, air conditioners, boilers and chillers
and more space for building owners.
It reduces the waste of energy by combining the production of heat and
power in a single thermodynamic process, i.e., cogeneration. A
typical nuclear power plant, for instance, only uses about 40 percent
of the fuel it burns to produce electricity while the rest of the fuel
is wasted up the smokestack. Cogeneration or combined heat and power
(CHP) can recover most of this wasted heat and use it to heat buildings
in the surrounding area. Cogeneration is not only more environmentally
sound, it means lower operation and maintenance costs, more reliability,
higher thermal comfort, and more design flexibility.
Advantages
of the shell and tube
heat exchanger:
At the center of every district heating and cooling system is the
heat exchanger. The transfer of heat from from the hot water to the internal
heating system of a building is best accomplished by a shell and coil
heat exchanger where high heat transfer rates, compact design and low
maintenance costs are high priorities. They are are often used in district
heating sub-stations as tap water heaters and in space heating loops.
- High Performance: the unique coil arrangement has a large heat transfer area meaning high heat tranfer coefficients.
- Compact and Lightweight: closely packed tubes makes our shell and coil exchangers compact and lightweight. Small footprint makes it easy to install in district substations where space is limited and hard to access.
- Low Maintenance Costs: corrugated tube design produces a high turbulent flow, which reduces deposit build-up and fouling. This means longer operating cycles between scheduled cleaning intervals.
- Low Installation Costs: vertical installation makes it ideal for hydronic systems like district heating and cooling systems where space is an issue.
- Higher Temperature Differentials: helical design allows for higher temperatures and extreme temperature differentials without high stress levels and costly expanision joints.
- Low Pressure Drop:
- Easy selection based on sub-station space requirements and heat or cooling load.
- Units kept in stock for immediate delivery.
Please note that all shell and coil heat exchangers are available for immediate delivery.
Do you still have questions? We invite you to call or email us today for more information. We'll be happy to provide you with a heat exchanger that matches your specific needs.